Ohio Farm Bureau Podcast: White House conversations and trade updates
Hear about Adele Flynn’s recent trip to the White House and a trade update from The Ohio State University.
Read MoreAs trade questions persist, grain farmers and their overseas markets are ground zero in the debate.
As more and more headlines speak of trade tariffs, trade wars and import/export markets, it’s good to be reminded of what these issues mean to our farm friends, neighbors and businesses that call Ohio home. Ohio grown grain crops are ground zero in this debate.
Ohio products are in demand in many foreign countries and grain is certainly no exception. Exports are big business for the state’s agriculture economy. Ohio exported more than $2 billion in oil seed and miscellaneous grain in 2016, up 21.2 percent over 2015, according to the Ohio Development Services Agency. North American markets traditionally are strong, and corn and soybeans have been selling well in Asian markets given the state’s connection to the Ohio River, which links to several domestic ports.
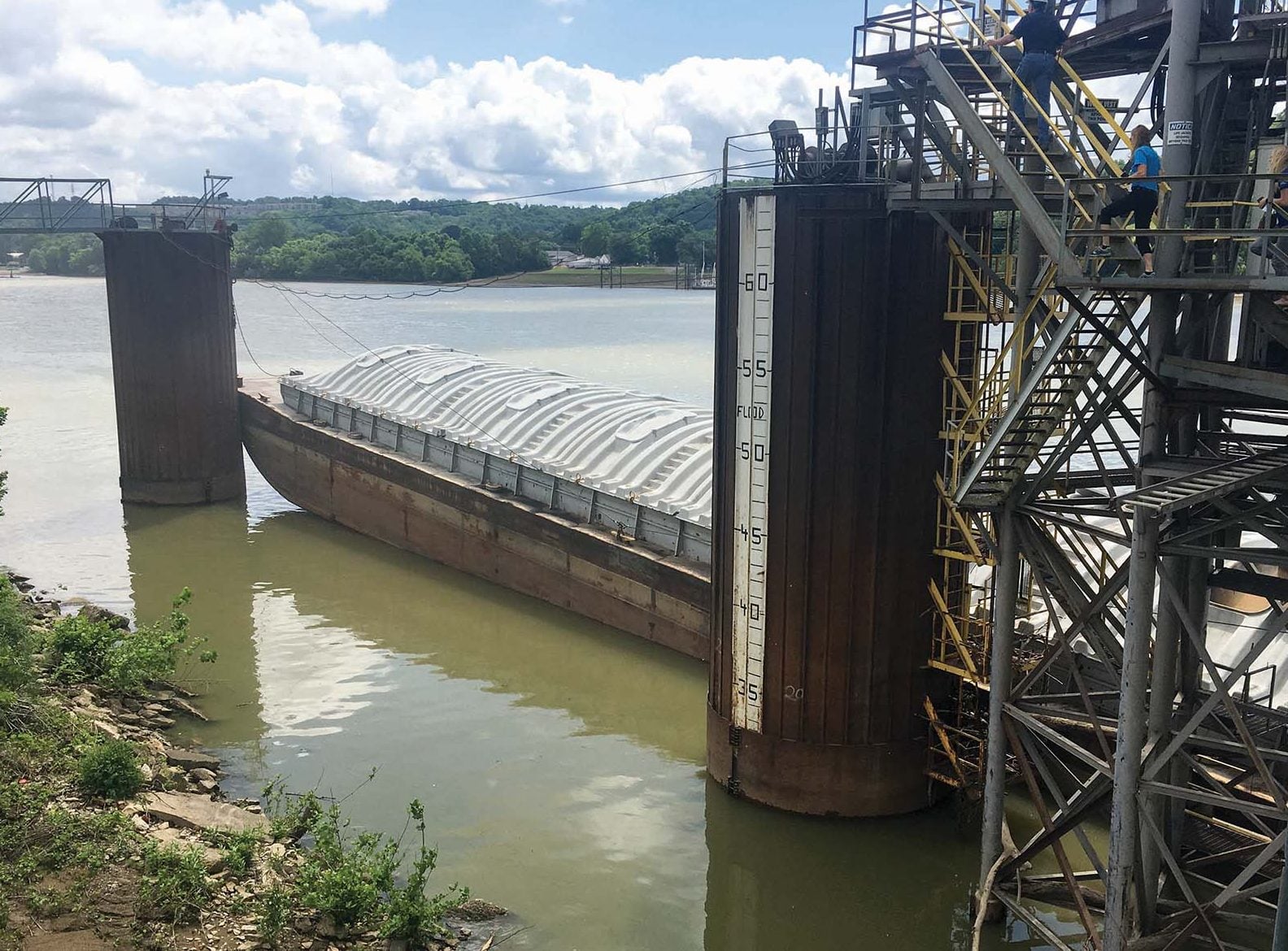

“It’s the entry point for a lot of our agricultural commodities into the international trade market,” said Brandon Kern, Ohio Farm Bureau’s senior director for policy outreach.
Ohio Farm Bureau held a conference in 2017 in Cincinnati that examined trade, water infrastructure, NAFTA and other important issues surrounding the movement of agricultural goods from Ohio to international markets. It’s an industry that includes not only farmers and those who use their grain, but also the companies that move the goods from point A to point B.
They include Consolidated Grain and Barge, a Japanese-owned commodity trading company. CGB operates several facilities along the Ohio River in and near Cincinnati that help farmers distribute their goods to customers in foreign countries.
CGB is owned by Zen-Noh Grain, the largest farmer-based cooperative in Japan, and multifaceted importer/exporter Itochu International. Ohio farmers’ corn and other products are often shipped to Zen-Noh, which in turn supplies local feed mills.
“CGB is that bridge, that network that can help Ohio farmers gain access to international markets,” said Tim Baumgart, CGB’s Ohio Valley region trading manager. “We have the assets along the river system that allow us to buy commodities out of Ohio, transport them along the inland waterway system and then hit many of the export destinations.”
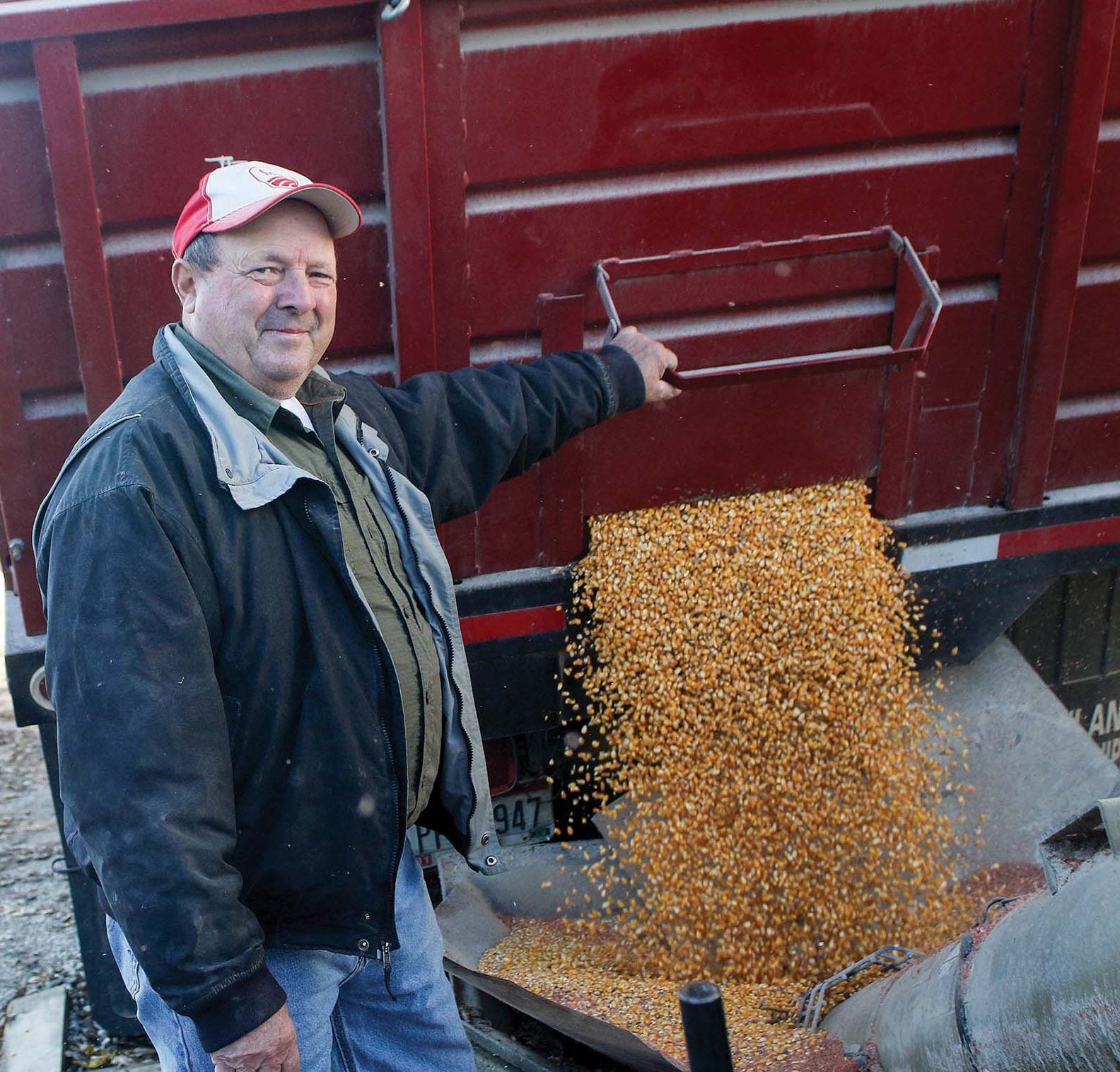

Ohio, like nearby Midwestern states, is known for producing high-quality products. But most foreign transactions are price-dependent. For instance, Baumgart said, some overseas soybean buyers will pay a bit extra for soybeans grown in Indiana, Ohio and Michigan. But ultimately, the lowest price drives the transaction, and the more competition that exists for Ohio products, the better the markets will be for farmers.
“China has been a large customer of U.S. soybeans in recent years,” Baumgart said. ”Ohio, given its connection to the river system, has been a good participant to fill some of the Chinese export demand.”
Hamilton County Farm Bureau member Dennis Heyob, who farms nearly 1,000 acres of corn and soybeans in western Hamilton County with his brother, Mike, got on board with exporting a decade ago when there was a demand for grain that was non-GMO. He’s contracted with Cargill to sell goods to customers in Japan.
“The end users were willing to pay a premium,” Heyob said. “It wasn’t much when we started, but it was better than nothing. We got in on the ground floor and have maintained our non-GMO production ever since.”
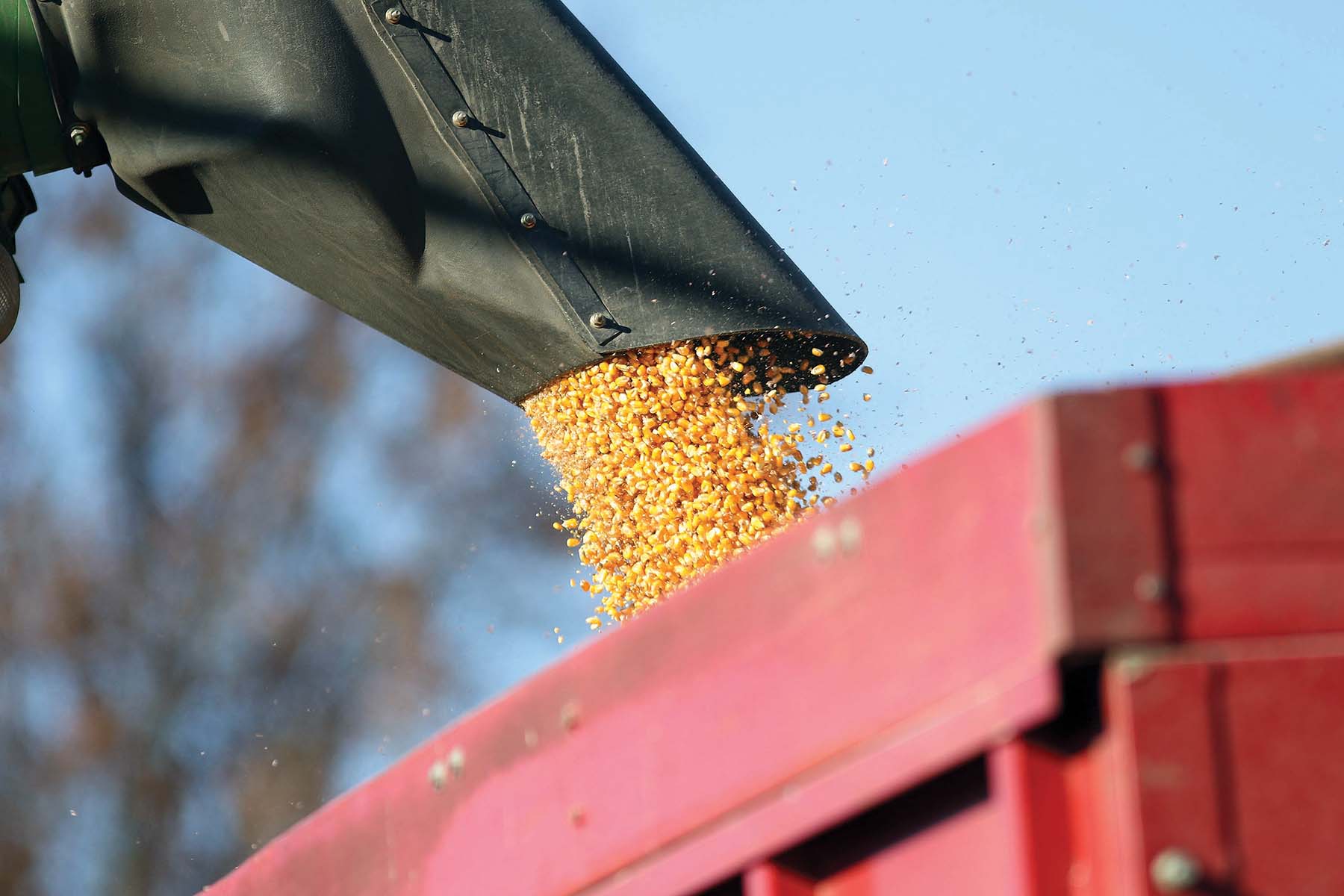

Today, Heyob sends almost all the grain they produce overseas, about 75,000 bushels of corn and 27,000 bushels of soybeans in 2017.
Selling overseas doesn’t take a degree in international business. The exporters handle the transportation issues and purchase the product. So farmers essentially call a representative such as Baumgart at CGB and request a bid for their grain.
Heyob said he and his brother export through Cargill.
“We sign a contract that we’re producing a non-GMO product,” he said. “It has to meet purity levels and everything else in the contract. After that they can sell it to whoever wants it.”
The grain elevators can condition the grain for moisture content and other variables before the product is loaded onto barges. CGB typically sends grain down the Ohio River to the Port of New Orleans.
Once there, the grain is sent to an export elevator that stores it and later reloads it onto a vessel (large ships that have several hollow holds). From there it reaches its foreign destination.
The smoothness of this methodical planning hinges on some important trade issues currently being discussed. They include this year’s potential renegotiation of the North American Free Trade Agreement, as well as action by the Trump administration to pull out of the Trans-Pacific Partnership in November 2016.
Ohio Farm Bureau is active in following several factors that can influence the export of Ohio grain.
One is the waterway system. Poor transportation infrastructure, such as that recently making news at Lock and Dam 52 in Paducah, Ky., can impede the timely export of goods. Breakdowns in the Ohio River lock have cost the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers more than $13 million and have backed up traffic.
“You see a lot of delays there,” Baumgart said. “Freight gets stuck above or below the lock and it closes.”
“We’re in competition with other origins,” Baumgart said. “The more we can stress quality in our export channel gives us more of an advantage to sell into those markets.”
Water quality also is an issue demanding the attention of Ohio farmers. Algae blooms, phosphorus runoff and nitrogen loss can impact farmers and Farm Bureau concentrates many of its advocacy efforts on that subject.
“A lot of things can affect the price of crops,” Heyob said. “It can be political, weather, insect outbreak, disease outbreak, drought; everything affects the price that’s in the marketplace. If there’s a hardship somewhere, the price will go up. If everybody has a good crop, the price goes down.
“We live by true supply-and-demand economics.”
International trade is important not just to Ohio farmers but also to the state’s overall economy.
“Exports are the most important market for a grain farmer today in Ohio,” said Tadd Nicholson, executive director of the Ohio Corn & Wheat Growers Association on an episode of Town Hall Ohio. “(Trade) is the biggest driver of profitability for a farmer right here in rural Ohio. Half of our wheat and more than half of our soybeans in this country go outside the United States.”
Ohio Farm Bureau and American Farm Bureau have been working as part of an industry-wide effort to send a message to Washington, D.C. and beyond about the importance of trade to the agricultural industry, specifically as it relates to the North American Free Trade Agreement and a looming trade war with China.
OFBF Executive Vice President Adam Sharp, along with colleagues from the Ohio Chamber of Commerce, Ohio Corn & Wheat Growers Association and economist Ian Sheldon, professor and Andersons chair of agricultural marketing, trade and policy for Ohio State University, have stressed the importance of trade with editorial boards at major Ohio newspapers over the last few months.
While NAFTA remains in negotiations, the 11 countries remaining in another multinational trade deal, the original Trans-Pacific Partnership, have moved on without the United States, signing a new agreement in March. The United States pulled out of the original TPP in January 2017.
In early April 2018 when the U.S-China trade rhetoric heated up, AFBF President Zippy Duvall said this: “Growing trade disputes have placed farmers and ranchers in a precarious position. We have bills to pay and debts we must settle, and cannot afford to lose any market, much less one as important as China’s.”
Read Ohio’s Export Report from 2023.
Farm Advantage provides you with the tools to help you market what you produce, manage your risk, maximize your margins and grow your business. Farm Advantage is a member benefit for Farm Bureau members.
Hear about Adele Flynn’s recent trip to the White House and a trade update from The Ohio State University.
Read More

Learn about an AFBF Market Intel report that explores different topics related to agricultural trade, including the potential impacts of trade policy changes.
Read More

Over 20% of all the production in the United States from agriculture gets exported to a different country.
Read More

Ohio Farm Bureau has collected information and resources that will be updated as the trade and tariff situation continues to unfold.
Read More

Learn more about how the Ohio Soybean Council is working with trade teams from around the world to find demand for Ohio grown soybeans and why more farmers are looking into forming LLCs.
Read More

Shortly after the crisis escalated, prices for corn, soybeans and wheat were trading limit-higher overnight.
Read More

Just as grain prices quickly climbed, so did the prices for other agricultural products.
Read More

Sen. Sherrod Brown hosted a virtual roundtable with Ambassador Katherine Tai, 19th United States Trade Representative, and Ohio farmers, workers and manufacturers to discuss the impact of trade policy on Ohio communities.
Read More

The economic impact of international trade extends far beyond the farms producing the crops.
Read More

Newton, chief economist at American Farm Bureau, talks about the latest news involving ag trade, farm profitability and future outlook on the farm economy.
Read More